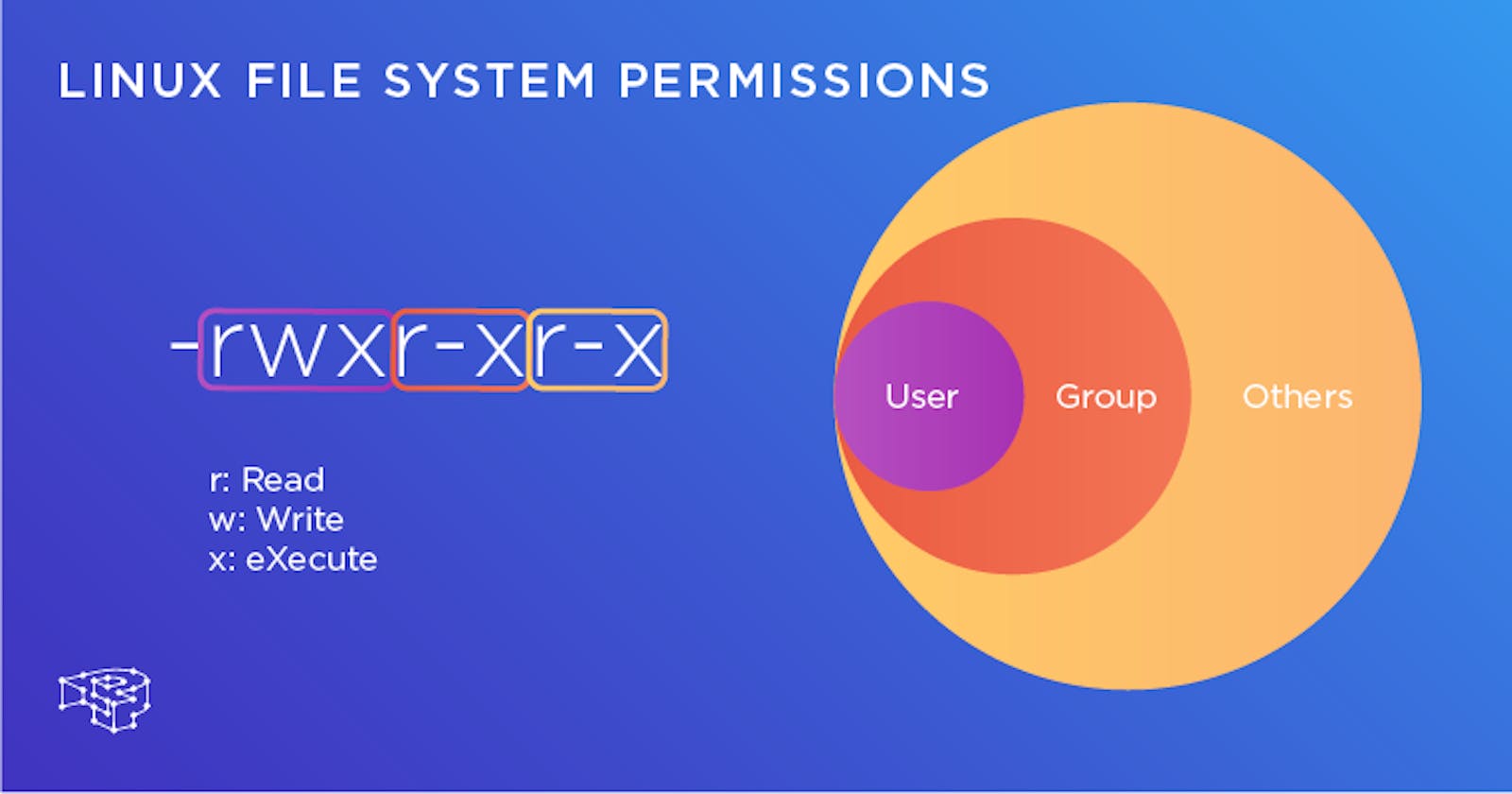
Today is more on Reading, Learning and Implementing File permissions.
Create a simple file and do ls -ltr to see the details of the files.

chown (change owner):
This is the command we can use to change who owns a particular file or directory.
chown <owner> <file>owner -> The owner we want to add or a new owner.
file -> The file we are trying to change.
file type:
The very first character indicates the type of file.
some of the common terms are as follows.
-- regular file.d- directory.c- character special file.l- symbolic link.
Regular files:
| terms | owner | group | word |
| - | rw- | rw- | r-- |
directory
| terms | owner | group | word |
| d | rwx | -wx | r-x |
character special file
| terms | owner | group | word |
| c | rwx | -w- | r-x |
Symbolic link
| terms | owner | group | word |
| l | rwx | -wx | r-x |
An article about File Permissions.
chmod:
To change the permission of a file or directory, we can use the chmod (change mode).To use chmod to alter permission, we need to tell.
For example. we have
file.txtwith some permission.
| owner | group | word |
| rw- | r-- | r-- |
so, now we will change the permission of the file.
command: chmod 777 file.txt
| owner | group | word |
| rwx | rwx | rwx |
Read about ACL and try out the commands getfacl and setfacl.
getfacl:
- The
getfaclrepresents the filename, owner, group, user’s permission, group’s permission, and others’ permission in a readable format.
setfacl:
- For adding permission to the user is done by
setfacl.